Histopathology
Histopathology
Histopathology is the main diagnostic branch of medicine, which examines the tissue disorders of the diseases and the root cause behind them. It involves the examination of tissues removed during medical procedures to determine the exact nature of the disease (non-tumor or tumor, benign or malignant lesion, etc.), the effectiveness of the surgical treatment (examination of the surgical margins), or the effectiveness of the applied treatments (e.g. post-prostate biopsy). Any tissue removed from a living individual should be subjected to a histopathologic examination to provide evidence of tissue lesions. The exceptions are the teeth and the placenta in physiological pregnancy.
Any tissue removed during a medical procedure is examined by a pathologist. Most of the daily routine is based on histological diagnostics, and reporting biopsies or surgical preparations. This routine histological diagnosis involves a number of additional testing methods, such as special staining procedures and immunohistochemical tests. Nowadays, they are an essential complement to the pathology tool that enables them to resolve differential diagnostic issues, diagnose pathogens, typify tumors, predict tumors, and design tailor-made treatments. Pathologists play a crucial role in the treatment of cancer patient. They evaluate not only the histological specimens, but they also take into account previous examinations and the patient's individual medical history, which together provide the basis for targeted therapy.
Intraoperative frozen section
The histological examination of the intraoperative frozen section has a crucial importance in determining the tumor-free status of the resection line, identifying lymph node metastases, defining the grading of the lesion and the need for surgical extension.

Processing the samples
The first step in histological processing is to start the sample. At the start, the pathologist describes the main features, size, tissues, organs, organ parts, lesions of the sample received, observes their surface, color, structure, texture, then with a sharp knife or blade cuts out the areas to be examined under the microscope. He also records the number of tissue blocks and cassettes cut for processing, the status of the remaining tissue sample, and the fixed or unfixed nature of the material. If necessary, he may apply ink staining to judge the edges of the excision and may require special procedures such as fat staining or decalcification.
Paraffin embedding
During tissue embedding, water is removed from the tissues and the sample is embedded in paraffin, which hardens the tissue and makes it incisionable.

Automata ágyazógép
A szövetbeágyazás során történik a szövetekből a víz elvonása, majd a minta kiöntése paraffinnal, mely a szövetet megkeményíti, és azt metszhetővé teszi.

Automata kiöntő gép (balra), illetve a folyamat további részei
Slide preparation
The molded paraffin block is cut with a machine called microtome. It is capable of cutting even sections of 2-5 µm thickness. These sections are then applied to glass slide.


Mikrotom (fent, lent jobbra), illetve vízfürdő a metszetek gyűrődésmentes felviteléhez a tárgylemezekre (balra)
The tissues in the sections are treated with different dyes and dye combinations for microscopic evaluation.
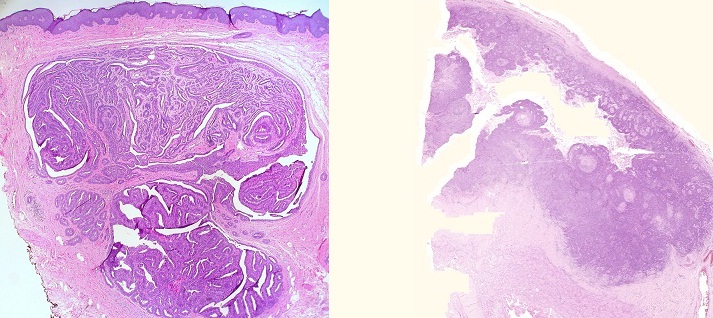
Jóindulatú elváltozás: hydradenoma vulvae (balra), rosszindulatú elváltozás: carcinoma planocellulare penis (jobbra)
If diagnosis of the lesion is not possible with conventional hematoxylin and eosin staining, additional special staining (PAS, alcove, van Gieson, Giemsa, Tsiebel, Grocott) may be required.

Hematoxylin-eozin festésre alkalmas automata berendezés (balra), illetve automata fedőgép (jobbra)
Immunohistochemistry may be required to make the correct diagnosis and to investigate the prognostic markers of tumors. The stained sections are covered with a tenth millimeter thick cover plate to ensure the long-term preservation of the texture and color of the sections.
Microscopic examination
During microscopic examination, the pathologist reviews the tissue sections and determines the location, structure and relationship of the normal tissue and the lesion, as well as the nature and properties of the cells. He may order specific staining or immunohistochemical examination. It is also possible to have a personal discussion with the physician, which can also be an important part of making an accurate diagnosis.
Purpose of Immunohistochemical (IHC) Marker Tests
During immunohistochemistry tissue antigens are detected by specific binding antibodies to infer primary tumor site, to detect metastases, to define degree of malignancy, to determine prognostic factors and therapeutic guidance.
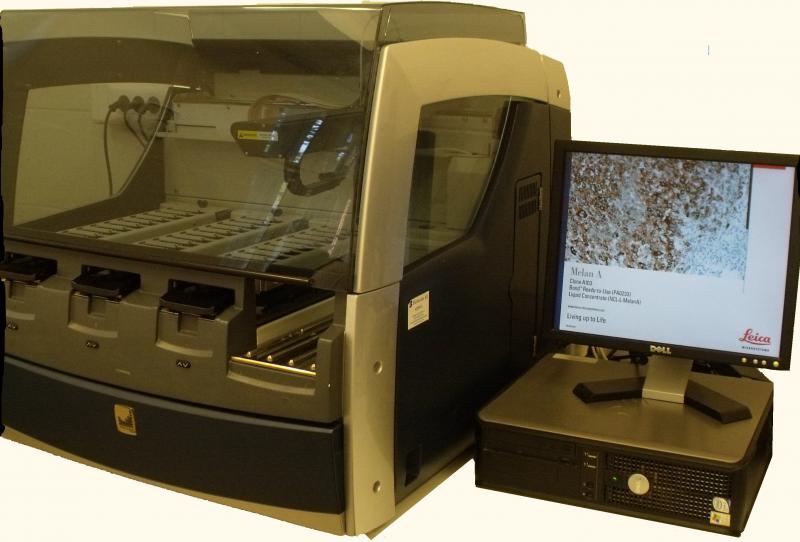

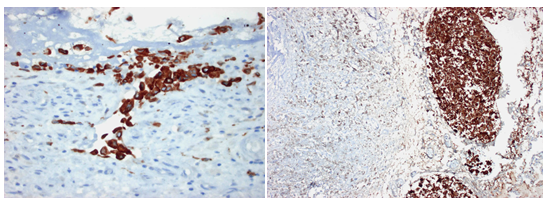
Carcinoma metastasisok kimutatása immunhisztokémiai vizsgálattal
Histopathological finding
The histopathological finding is the summary of the histopathological diagnostic work which includes the diagnosis, opinion and therapeutic recommendations.
Updated: 2020.01.10.


